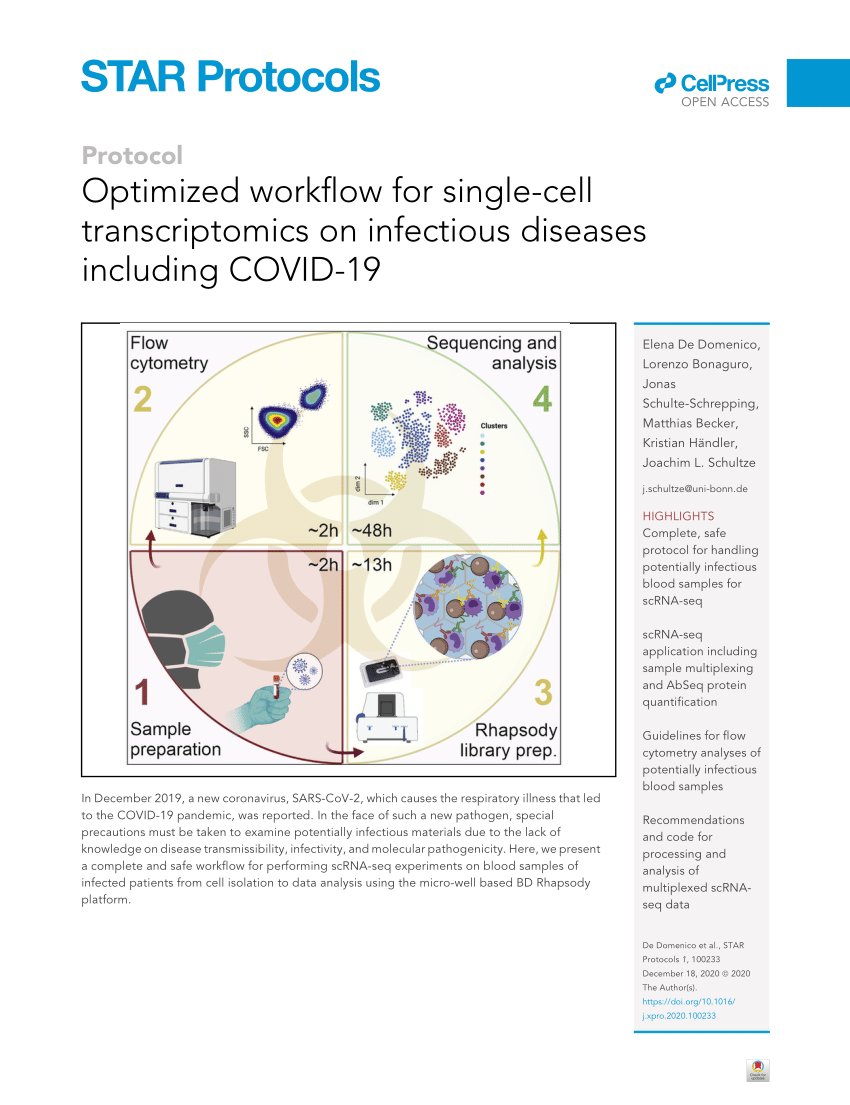
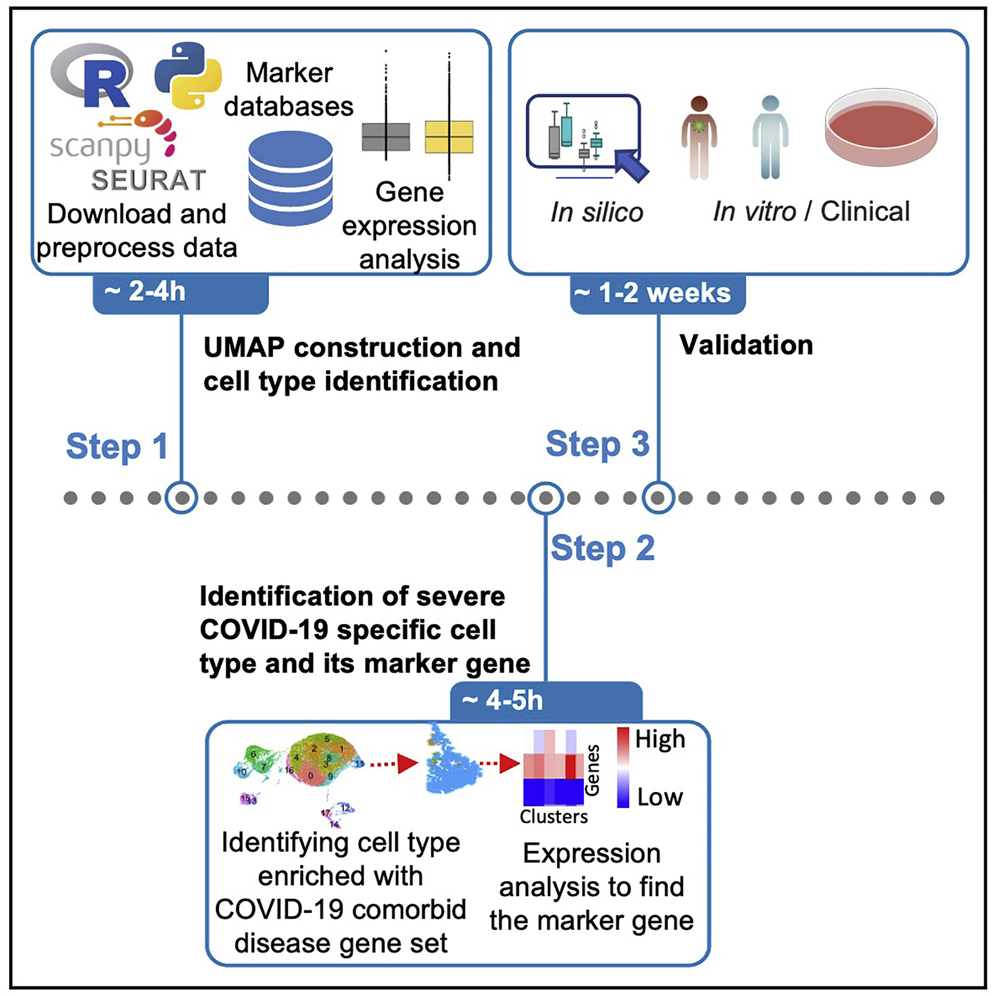
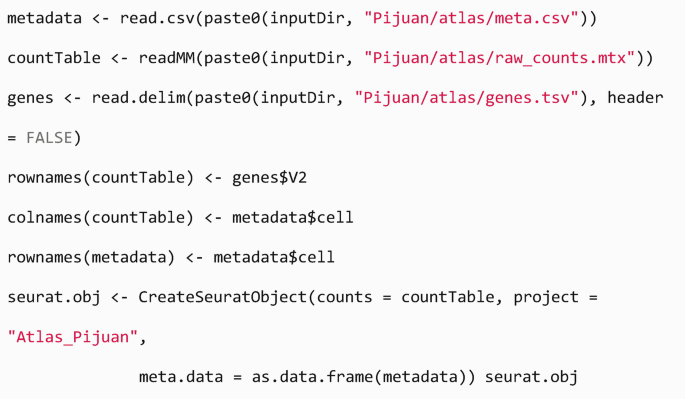
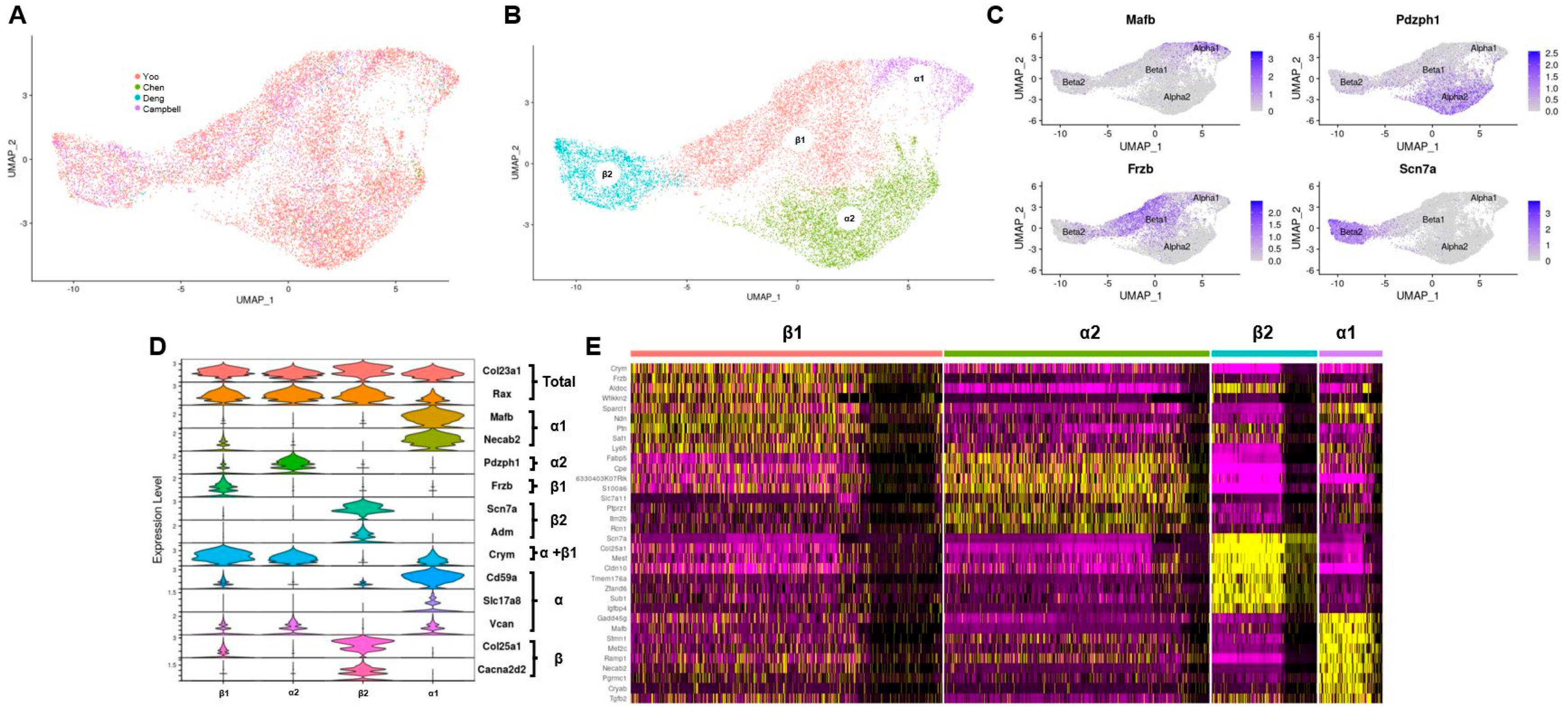
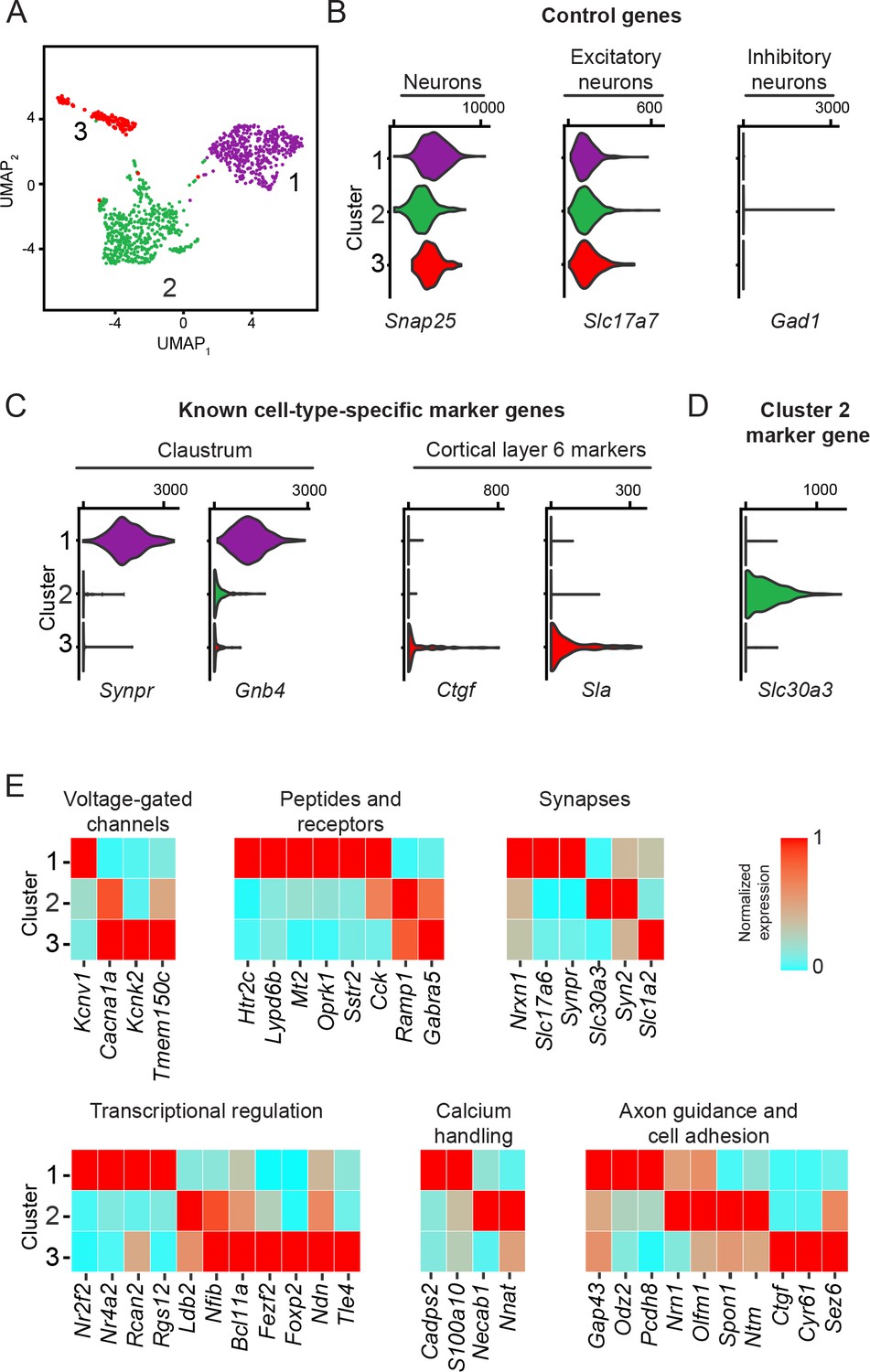
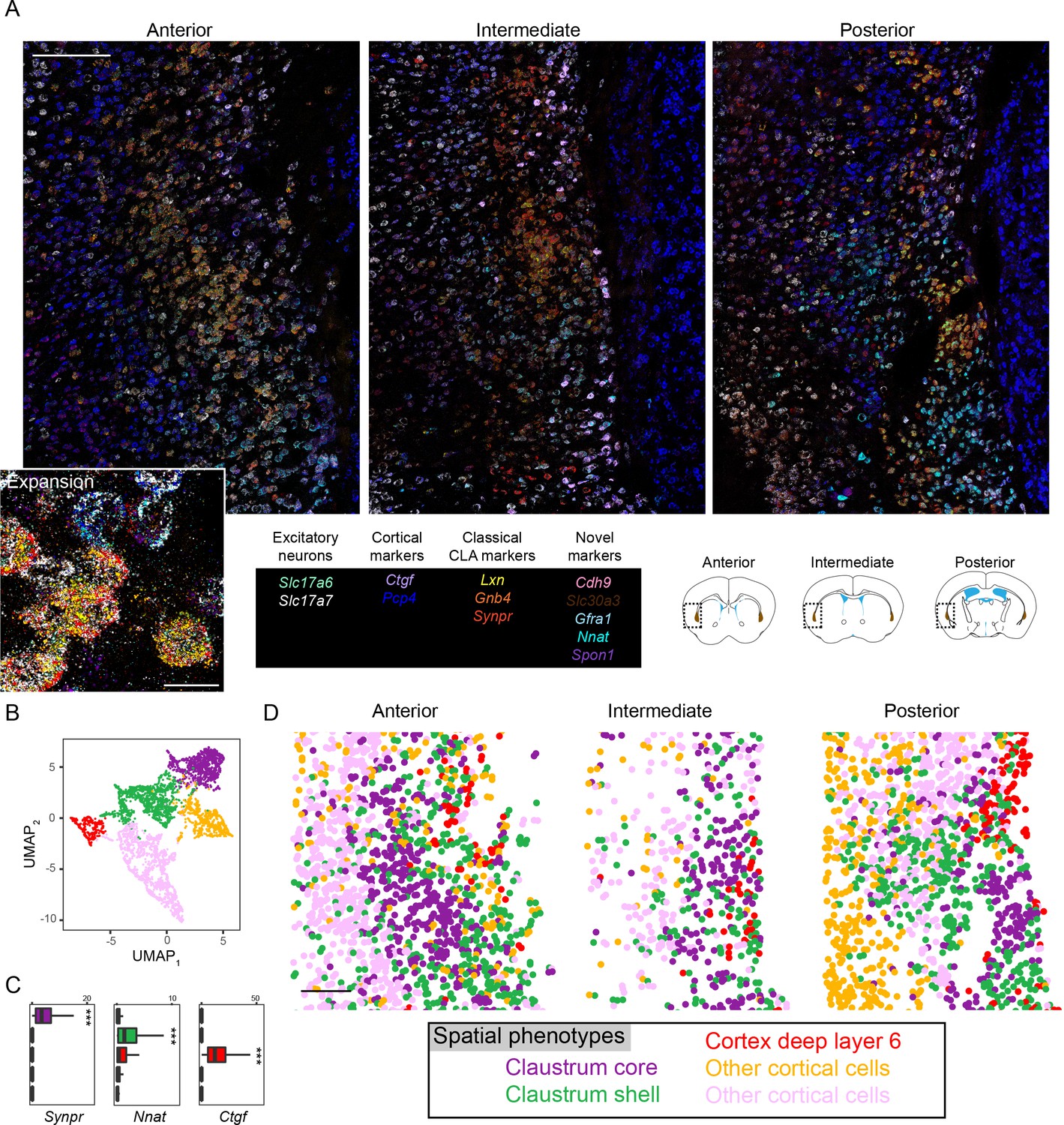
Sharp cell-type-identity changes differentiate the retrosplenial cortex from the neocortex - ScienceDirect
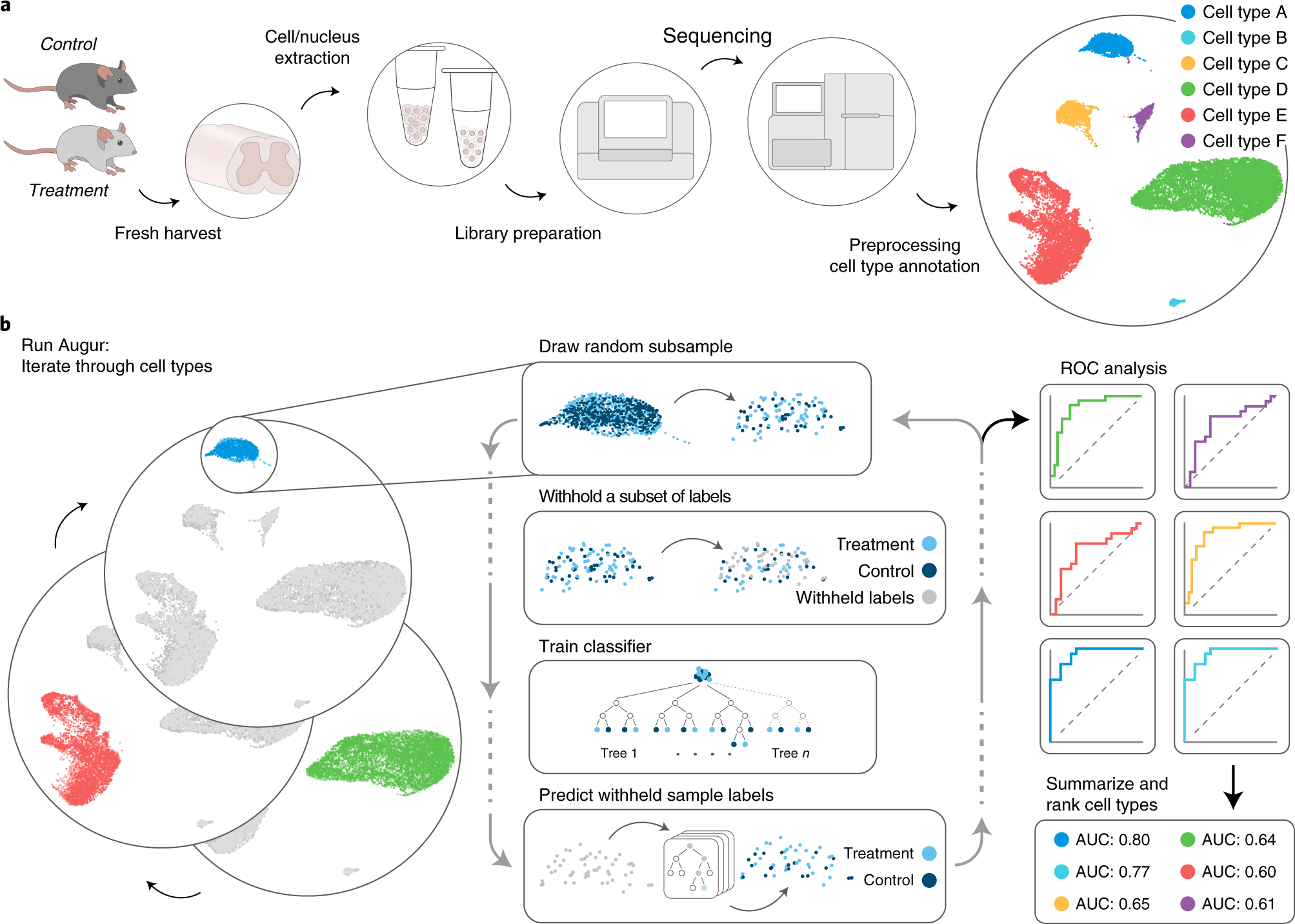
Prioritization of cell types responsive to biological perturbations in single-cell data with Augur | Nature Protocols

Single-cell microglial transcriptomics during demyelination defines a microglial state required for lytic carcass clearance | Molecular Neurodegeneration | Full Text

Single-Cell Transcriptomic Profiling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Modulation in Marfan Syndrome Aortic Aneurysm | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Preservation of co-expression defines the primary tissue fidelity of human neural organoids | bioRxiv
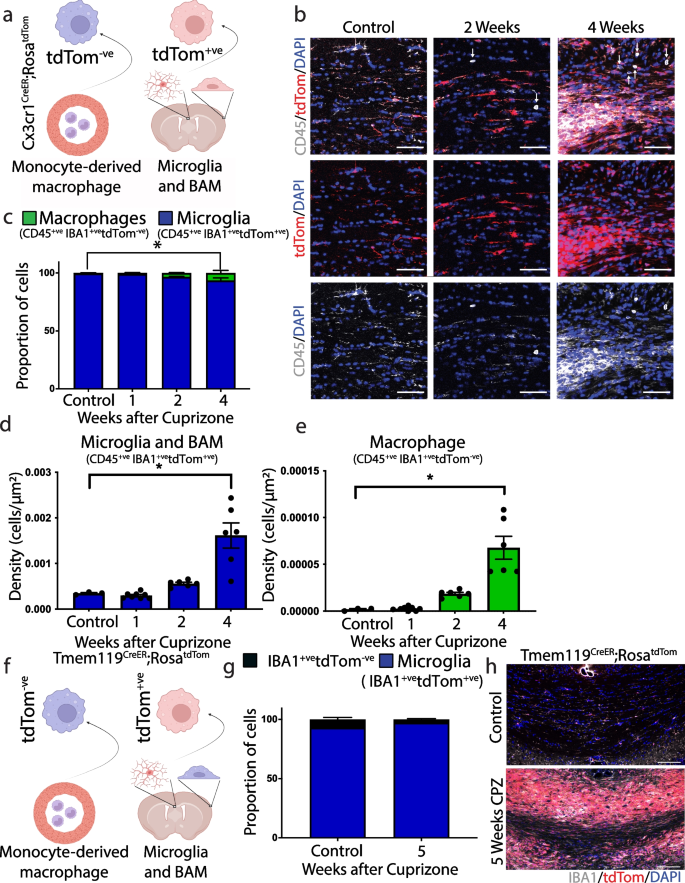
Single-cell microglial transcriptomics during demyelination defines a microglial state required for lytic carcass clearance | Molecular Neurodegeneration | Full Text

Single-Cell Transcriptomic Profiling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Modulation in Marfan Syndrome Aortic Aneurysm | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Single-nucleus transcriptomics of the prefrontal cortex in major depressive disorder implicates oligodendrocyte precursor cells and excitatory neurons | Nature Neuroscience

Preservation of co-expression defines the primary tissue fidelity of human neural organoids | bioRxiv
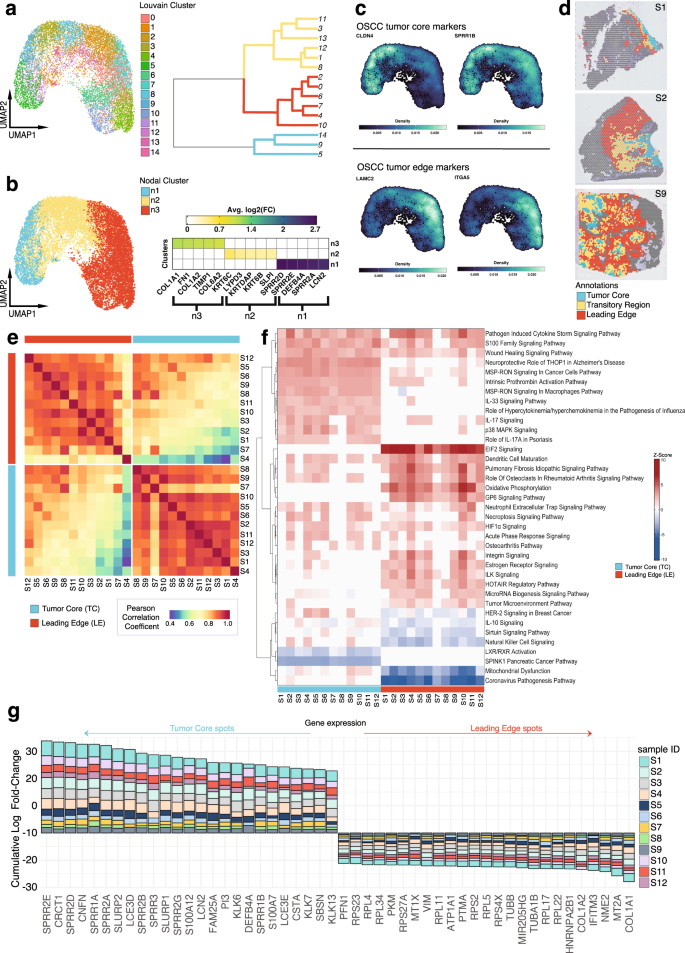
Spatial transcriptomics reveals distinct and conserved tumor core and edge architectures that predict survival and targeted therapy response | Nature Communications

PDF) Spatial transcriptomics reveals distinct and conserved tumor core and edge architectures that predict survival and targeted therapy response
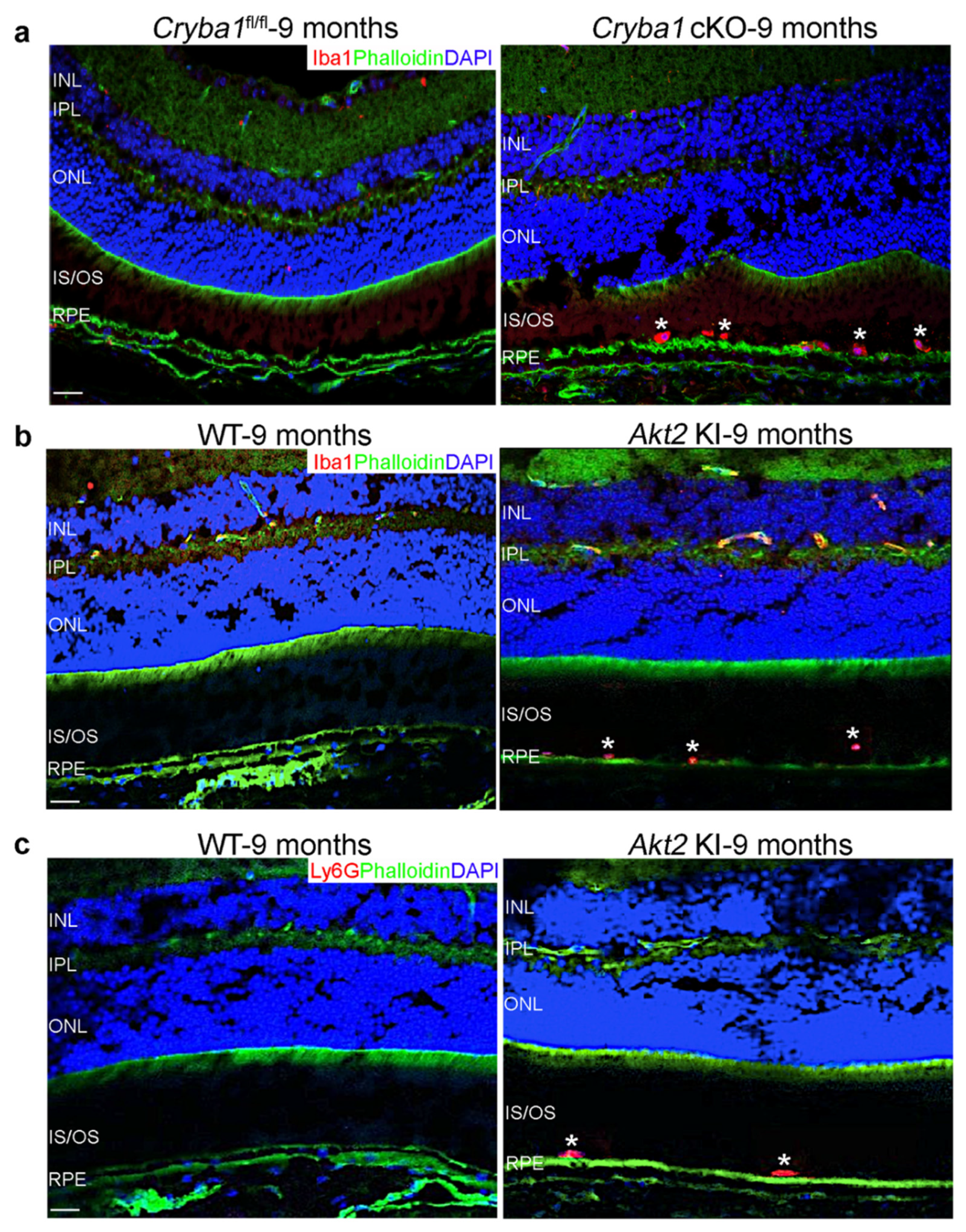
Cells | Free Full-Text | Microglia–Neutrophil Interactions Drive Dry AMD-like Pathology in a Mouse Model
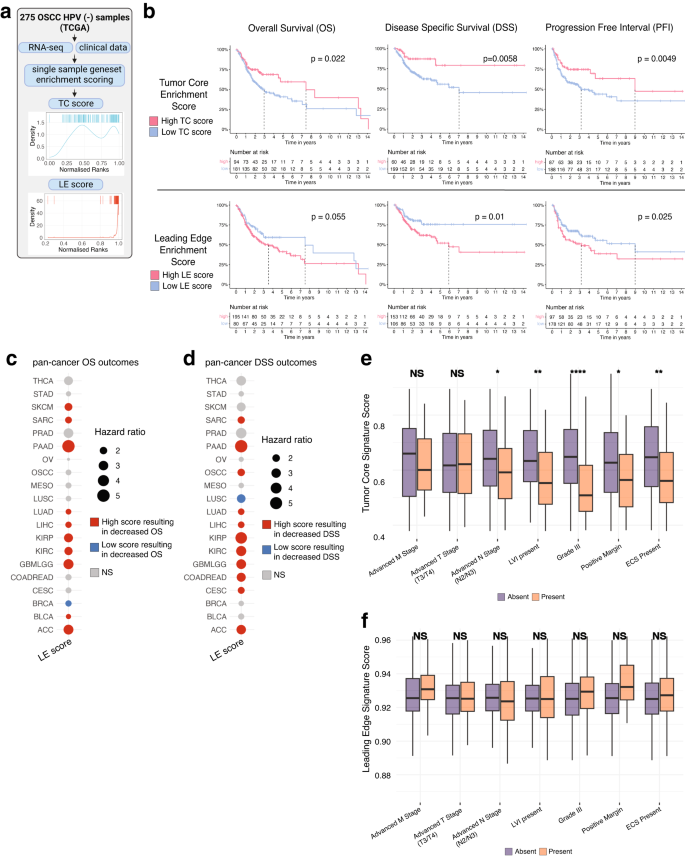
Spatial transcriptomics reveals distinct and conserved tumor core and edge architectures that predict survival and targeted therapy response | Nature Communications

Androgens show sex-dependent differences in myelination in immune and non-immune murine models of CNS demyelination | Nature Communications
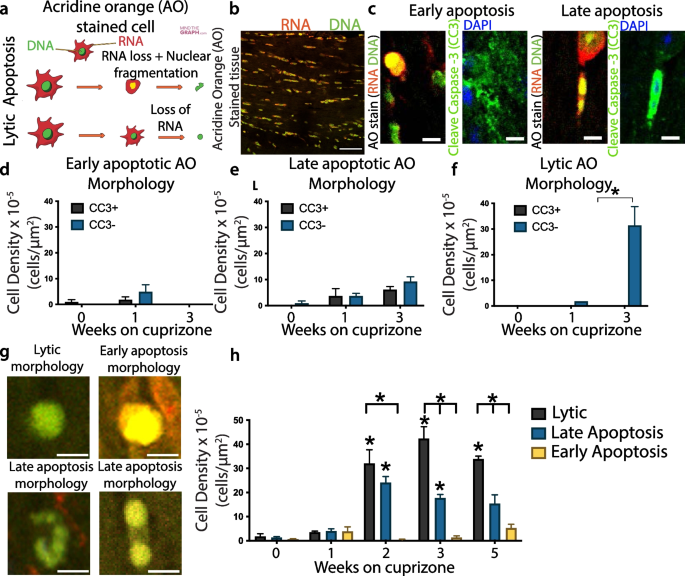
Single-cell microglial transcriptomics during demyelination defines a microglial state required for lytic carcass clearance | Molecular Neurodegeneration | Full Text

Lineage-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Smooth Muscle Cell Modeling Predicts Integrin Alpha-V Antagonism Reduces Aortic Root Aneurysm Formation in Marfan Syndrome Mice | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology